Illinois Dems ignore promises and embrace gerrymandering, approve controversial maps
The Princeton Gerrymandering Project, a nonpartisan group that evaluates maps, gave Illinois' maps an "F" grade, saying they give Democrats a significant advantage and are "very uncompetitive."
By SARA BURNETT | Associated Press
With additional information provided by staff at the Chicago Journal
CHICAGO (AP) — In the neck-and-neck fight to keep control of the U.S. House of Representatives, Democrats need help from the few places where state lawmakers can make 2022 difficult for Republicans.
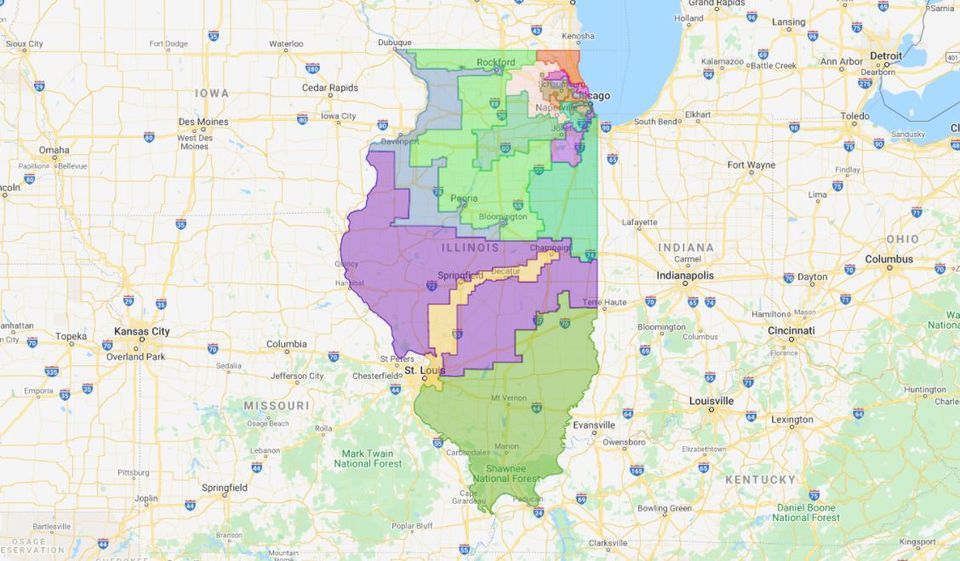
Illinois Democrats delivered Thursday, using their dominance in state government to advance new congressional district maps intended to eliminate two Republican-held districts and send more Democrats to Washington.[1]
To do it, Illinois Democrats have embraced gerrymandering, the practice of drawing district boundaries for political benefit that party leaders including former President Barack Obama and former Attorney General Eric Holder have railed against as "rigging" elections. The new map is a collection of odd shapes resembling abstract art and, critics say, a symbol of Democrats' hypocrisy.
"This is a desperate map from a desperate party," said Adam Kincaid, executive director of the National Republican Redistricting Trust, which coordinates redistricting for the GOP. He called it "America's most extreme gerrymander."
Both parties use gerrymandering, though Democrats more actively opposed it after the GOP used the practice in 2011 to create advantages for the next decade. Obama traveled to the Illinois Capitol where he once served as a state senator to deliver a speech about America's broken political system, saying gerrymandering — packing a party's supporters into one district or dispersing the other party's voters for political advantage — was the reason nothing could get done in Congress.
Democrats in some states even gave up their own power by pushing for independent commissions to draw boundaries.[2] And Holder became chairman of the National Democratic Redistricting Committee, which has backed legal challenges to GOP-drawn maps in places like North Carolina and Virginia.
Democrats in Illinois, meanwhile, have done all they can to exert control and ensure it benefits their candidates for elections through 2030. Even with Illinois losing a seat due to population loss, the map was drawn to create a congressional delegation of 14 Democrats and three Republicans starting in 2022, a change from the current 13-5 split. The Princeton Gerrymandering Project, a nonpartisan group that evaluates maps, gave Illinois' maps an "F" grade, saying they give Democrats a significant advantage and are "very uncompetitive."

The maps — along with maps in other Democrat-controlled states like New York — could be pivotal as Democrats try to hold their narrow majority in next year's midterms, when the party in the White House has historically performed poorly. Republicans are in charge of the mapmaking known as redistricting in more than twice the number of states as Democrats, including large, growing states like Texas and Florida.
Illinois Democrats defended the maps they released late Thursday and passed a short time later, saying they ensure minorities and other Illinois residents have an equal voice in government.
"I'm proud of this map," said Illinois Senate President Don Harmon, a sponsor of the redistricting legislation. "This is a fair map and it reflects the diversity of the state of Illinois." He also said lawmakers chose to unite communities "that shared political philosophies and policy objectives."
Democrats added a second predominantly Latino district, after census data showed Illinois' Latino population grew over the past decade. They also maintained three predominantly Black districts.
An Illinois chapter of the NAACP disagrees. They filed a lawsuit last Friday alleging racial bias in the redistricting of House District 114.[3] They further argued that the new map jeopardizes the prospects of a candidate preferred by black voters, and is an effort to undermine and disenfranchise the black electorate.
GOP Reps. Adam Kinzinger, one of 10 House Republicans to vote to impeach former President Donald Trump, and Darin LaHood were put into the same heavily Republican district, as were GOP Reps. Mike Bost and Mary Miller.
Republican Rep. Rodney Davis, who said he may challenge Democratic Gov. J.B. Pritzker next year depending on the final map, was drawn into a safe GOP district that meanders from one side of the state to the other. It surrounds another Democrat-leaning district that was carved as a narrow squiggle stretching nearly 200 miles (322 kilometers) from the home of the University of Illinois to Democrat-friendly communities east of St. Louis. A former aide to Pritzker who worked in the Biden administration, Democrat Nikki Budzinski, is running for the seat.
Not all Democrats are happy. First-term Democratic Rep. Marie Newman was drawn into the same majority-Latino district as Rep. Jesus "Chuy" Garcia, a late-in-the-game move that Newman said was done "to appease one person and a small handful of affluent insiders at the expense of workers and working families" in her current district.
Democrats say that move — sacrificing one of their own party — proves the new maps are fair and should survive expected court challenges.
The Illinois Senate approved the maps late Thursday, with all Republicans voting no, and it later passed the House.
Democrats' aggressive mapmaking started earlier this year, when they insisted on approving new state legislative maps — which will strengthen their hold on the state House and Senate for another decade — using population estimates rather than census bureau data, making Illinois the only state in the nation to do so. Legislative leaders said they faced a deadline set by the state constitution, but that deadline was only for Democrats to have total control of the process, rather than a bipartisan commission.
Lawmakers had to redo those maps after census data showed they were unconstitutional because the districts varied dramatically in population.[4] Lawsuits seeking to have the new maps thrown out are pending.
Pritzker signed both the first set of legislative maps and the do-over maps, despite pledging during his 2018 campaign that he would veto any legislative maps drawn by politicians. He is expected to sign Democrats' congressional maps as well.

The Chicago Journal added some additional references to the original report from the AP.
Notes & References
Chicago Journal. “Illinois Democrats Unveil Updated Congressional Maps.” Chicago Journal. Chicago Journal, October 24, 2021. https://www.chicagojournal.com/illinois-democrats-unveil-updated-congressional-maps/. ↩︎
Riccardi, Nicholas. “Democrats See Consequences from Redistricting Reform Push.” AP NEWS. Associated Press, September 4, 2021. https://apnews.com/article/redistricting-579984fa53d997956749eb3d3820276b. ↩︎
Press, Associated. “Illinois NAACP Chapter Files Lawsuit Alleging Racial Bias in New Democrat Drawn Redistricting Maps.” Chicago Journal. Chicago Journal, October 17, 2021. https://www.chicagojournal.com/illinois-naacp-chapter-files-lawsuit-alleging-racial-bias-in-new-democrat-drawn-redistricting-maps/. ↩︎
Burnett, Sara. “Illinois Democrats to Redraw Political Maps Using Census.” AP NEWS. Associated Press, August 21, 2021. https://apnews.com/article/census-2020-illinois-2b3be094169e90afd4fcb147f509d859. ↩︎





